What are human endocannabinoids?
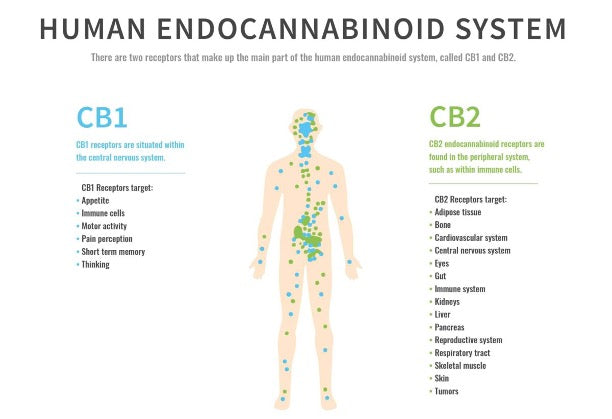
Human endocannabinoids are naturally occurring cannabinoids that are produced by the human body. They are part of the endocannabinoid system, which is a complex cell-signaling system that regulates a wide range of physiological and cognitive processes, including mood, appetite, pain, and sleep.
The two best-known endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). Anandamide is often referred to as the “bliss molecule” because it is associated with feelings of happiness and well-being. It is produced in areas of the brain that are involved in memory, motivation, and higher thought processes. 2-AG, on the other hand, is more abundant in the brain and is involved in the regulation of immune function and pain sensation.
Endocannabinoids are produced on demand in response to certain stimuli, such as stress, exercise, and pain. Once produced, they bind to cannabinoid receptors in the body, including CB1 and CB2 receptors, to produce various effects. The endocannabinoid system is complex and not fully understood, but it is believed to play a role in a wide range of physiological and cognitive processes, including appetite, pain, mood, and immune function. When you consume cannabinoids you activate and balance this system.